How Windows manages playing multimedia
Windows automatic behaviour
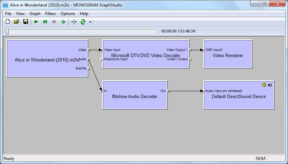 Quando un file viene giocato su Win-dows, most player software simply lets Windows handle the playback (Media Player Classic Home Cinema is an exception). Windows automatically selects an appropriate splitter to “split” the container, and then selects the appropriate decoders to decode each of the streams. Each decoded stream is then sent to a final stage known as a renderer. The splitter, decoders and renderers are known as filters and are sometimes referred to as codecs. The term codec has several common uses, but is generally used to mean a program which can carry out either encoding or decoding. In this guide we will use the term codec to refer to complete software packages, which may contain multiple filters and support multiple stream types. Each filter is a self-contained unit, usually stored inside an .ax file in the system32 folder. The process of selecting the splitter, decoders and renderers is known as building a graph. There are utilities available which allow you to see what graphs Windows will build for a particular file, così come la costruzione grafici personalizzati per provare la riproduzione
Quando un file viene giocato su Win-dows, most player software simply lets Windows handle the playback (Media Player Classic Home Cinema is an exception). Windows automatically selects an appropriate splitter to “split” the container, and then selects the appropriate decoders to decode each of the streams. Each decoded stream is then sent to a final stage known as a renderer. The splitter, decoders and renderers are known as filters and are sometimes referred to as codecs. The term codec has several common uses, but is generally used to mean a program which can carry out either encoding or decoding. In this guide we will use the term codec to refer to complete software packages, which may contain multiple filters and support multiple stream types. Each filter is a self-contained unit, usually stored inside an .ax file in the system32 folder. The process of selecting the splitter, decoders and renderers is known as building a graph. There are utilities available which allow you to see what graphs Windows will build for a particular file, così come la costruzione grafici personalizzati per provare la riproduzione
Ren-der-tori
 Ren-der-tori sono la fase finale del grafico; e sono l'interfaccia tra i flussi decodificati e l'hardware che emette il flusso - per esempio i driver della scheda video, or the sound card drivers. They manage the way the output fits into the Windows system. So for example you may play back a video in a window (al contrario di schermo intero) and also have another program open. Windows needs to how big to display the video, and where on the screen. You may also move another program or window partially in front of the video and Windows needs to know to discard this part of the video. This is all managed by the renderers.
Ren-der-tori sono la fase finale del grafico; e sono l'interfaccia tra i flussi decodificati e l'hardware che emette il flusso - per esempio i driver della scheda video, or the sound card drivers. They manage the way the output fits into the Windows system. So for example you may play back a video in a window (al contrario di schermo intero) and also have another program open. Windows needs to how big to display the video, and where on the screen. You may also move another program or window partially in front of the video and Windows needs to know to discard this part of the video. This is all managed by the renderers.
[google_adsense]
Decodifica Hard-ware
 Il suo-tor-ic-alleato tutti decodifica-zione è stata fatta dal CPU. Il CPU è progettato per essere molto flessi-bile, che significa che può sotto-prendere qualsiasi operazione, but is not especially efficient at anything. The increase in HD video content which requires substantial processing to decode has led to a demand for more efficient video decoding hardware. All modern video cards now include some level of “hardware decoding” of the 3 BluRay nor-me-zione ENCOD (mpeg2, h.264, VC1). The level of support varies but with each new generation of hardware more standards are supported. The latest generation of CPUs from Intel now also include dedicated decoding hardware which frees the main parts of the CPU for other tasks, and reduces power consumption. Dedicated GPU e CPU hardware decoding can only be utilised if the codec used for decoding supports hardware decoding. The level of support for this feature is variable, ma è crescere-ing, and several of the free codecs provide good support. The codecs Microsoft provides with Windows also offer some support. The system of hardware acceleration is commonly known as DXVA (-A-zione Accel-er Dir-ECTX Video). Molti recenti decoder hardware dedicati supportano anche le varie caratteristiche ottimizzazione delle immagini.
Il suo-tor-ic-alleato tutti decodifica-zione è stata fatta dal CPU. Il CPU è progettato per essere molto flessi-bile, che significa che può sotto-prendere qualsiasi operazione, but is not especially efficient at anything. The increase in HD video content which requires substantial processing to decode has led to a demand for more efficient video decoding hardware. All modern video cards now include some level of “hardware decoding” of the 3 BluRay nor-me-zione ENCOD (mpeg2, h.264, VC1). The level of support varies but with each new generation of hardware more standards are supported. The latest generation of CPUs from Intel now also include dedicated decoding hardware which frees the main parts of the CPU for other tasks, and reduces power consumption. Dedicated GPU e CPU hardware decoding can only be utilised if the codec used for decoding supports hardware decoding. The level of support for this feature is variable, ma è crescere-ing, and several of the free codecs provide good support. The codecs Microsoft provides with Windows also offer some support. The system of hardware acceleration is commonly known as DXVA (-A-zione Accel-er Dir-ECTX Video). Molti recenti decoder hardware dedicati supportano anche le varie caratteristiche ottimizzazione delle immagini.
In molti casi, decodifica hardware non è compatibile con l'uso di sottotitoli, how-mai, DXVA con sottotitoli è possibile tramite il libero open-source ffdshow tryouts.
Stream output Raw
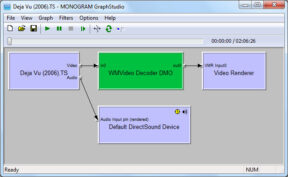 In some cases no decoder is required. Some audio on BluRay disks is uncompressed and can be sent directly from the splitter to the renderer without need of a decoder. In addition to this, many home theatre amplifiers include digital connectors (SPDIF o HDMI) e hanno i propri decoder hardware per l' 2 piombo-zione sistemi: Dolby and DTS. If you have an amplifier which supports hardware decoding you may wish to leave the audio stream encoded and send the encoded stream to the amplifier for decoding. To do this the stream from the splitter must be sent to the appropriate hardware (sia una scheda audio nel caso di SPDIF, o la scheda video HDMI). This stream must be sent in the correct way so the hardware knows to output it over the digital connection. To do this still requires a filter, but the filter will not decode the stream. The most common codec used for this purpose is called ac3filter.
In some cases no decoder is required. Some audio on BluRay disks is uncompressed and can be sent directly from the splitter to the renderer without need of a decoder. In addition to this, many home theatre amplifiers include digital connectors (SPDIF o HDMI) e hanno i propri decoder hardware per l' 2 piombo-zione sistemi: Dolby and DTS. If you have an amplifier which supports hardware decoding you may wish to leave the audio stream encoded and send the encoded stream to the amplifier for decoding. To do this the stream from the splitter must be sent to the appropriate hardware (sia una scheda audio nel caso di SPDIF, o la scheda video HDMI). This stream must be sent in the correct way so the hardware knows to output it over the digital connection. To do this still requires a filter, but the filter will not decode the stream. The most common codec used for this purpose is called ac3filter.
Video is never normally raw and so always requires a decoder filter. It must also pass through the renderer. Subtitle information is also passed to the renderer for rendering on top of the video.
Nuovo codec sistema in Vista
The system Windows uses to manage all these filters is called DirectShow. The vast majority of filters are designed to conform to the DirectShow standards. However, sotto Windows Vista, Microsoft introduced a new system called Media Foundation. This new system runs in parallel with DirectShow, but takes precedence. Microsoft has include Media Foundation codecs in all Windows releases since Vista, e quando un file viene riprodotto, Windows will try to use the Media Foundation codecs to playback the file. This has made it more difficult to use alternative codecs.


“Hi James I realise it has been a long while, but I just checked this on windows 11 (build 23H2)…”